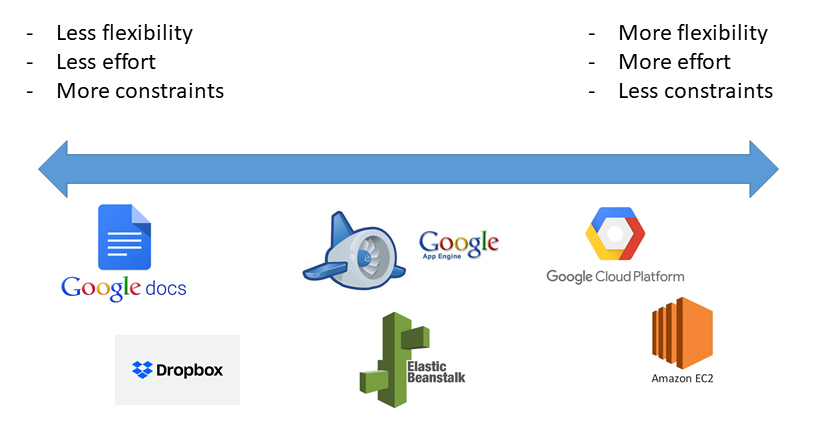
Why Cloud
Overview
Teaching: 0 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
Should we move to the cloud or should we stay on-premise?
Objectives
Understand necessity for cloud
1. What services does Cloud offer?
- Before we can evaluate the necessity of moving to the cloud, we need to to know what services are available.
- SaaS: Software-as-a-Service
- PaaS: Platform-as-a-Service
- IaaS: Infrastructure-as-a-Service
- Vendor: cloud service provider.
2. SaaS: Software-as-a-Service
- Vendor controlled applications that are accessed over the network by users.
- Characteristics:
- Network-based access
- Multi-tenancy
- Single software release for all
- Examples:
- Applications in the Google Suite
- Dropbox
- Cisco WebEx
3. SaaS: Application Design
- Net native
- Cloud-specific design, development, and deployment
- Multi-tenant data
- Built-in metering and management
- Browser-based
- Customization via configuration
- High degree of configurability, efficiency, and scalability
4. SaaS: Disadvantages
- SaaS providers are dependent on network and cloud service providers.
- Performance is dependent on individual client’s bandwidth.
- Security
- Good: Better security than personal computers
- Bad: SaaS vendors (and cloud providers) are in charge of the data
- Ugly: Privacy
4. SaaS and Privacy
- Who owns your data in SaaS?
- Google Drive ToS
5. SaaS and Privacy
- Who has access to your data in SaaS?
- Google ToS
6. PaaS: Platform-as-a-Service
- Vendors provide development environment.
- Tools and technologies are selected by vendors.
- Users maintain control over data (application) life-cycle.
- Examples:
- Google App Engine
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Heroku
7. PaaS: Architectural characteristics
- Support multi-tenancy at various scale: sessions, processes, and data.
- Isolation at: physical, virtual, and logical levels
- Microsoft’s offerings of isolation choices
- Native scalability
- Load balancing and fail-over (AWS Elastic Beanstalk)
- Native integrated management
- Performance
- Resource consumption/utilization
- Load
7. PaaS: Disadvantages
- Inherits all from SaaS
- Options on technologies and tools are limited by the PaaS vendors
8. IaaS: Infrastructure-as-a-Service
- Vendors provide computing resources.
- Users provision computing resources.
- Compute resources include processing, storage, memory, network etc.
- Users are provided with customized virtual machines.
- Users maintain control over:
- Operating system, memory
- Storage,
- Servers and deployment configurations, and
- Some limited control over network resources via software-defined networking
8. IaaS: Advantages
- Infrastructure scalability
- Native-integrated management via vendors’ utilities
- Performance, resource consumption/utilization, load
- Economical cost
- Hardware, IT support
9. IaaS: Disadvantages
- Require more technical efforts than SaaS and PaaS.
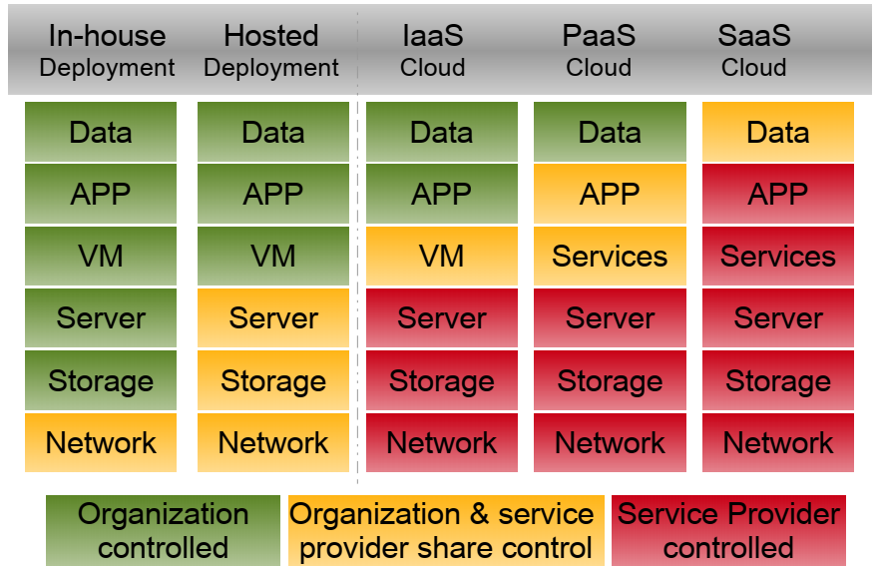
10. Comparing service models
11. Comparing services models
12. XaaS: Everything-as-a-Service
- Composite second level services
- NIST Evaluation of Cloud Computing Services (2018) p. 20
13. NIST: Four deployment models
- Private Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
14. Private cloud
- Infrastructure is organized solely for an organization
- Infrastructure is managed by the organization or by a third party
15. Community cloud
- Supports a specific community
- Infrastructure is shared by several organizations
- Examples: CloudLab
16. Public cloud
- Infrastructure is made available to the general public
- Infrastructure is owned by an organization selling cloud services
- Example: Azure Notebook free tier.
17. Hybrid cloud
- Infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds deployment models.
- Enables data and application portability
18. Cloud Security: who is doing what
- The cloud provider is responsible for the security OF the Cloud.
- The cloud consumer (users) is responsible for the security IN the Cloud.
19. Cloud consumer
- SaaS/PaaS:
- Standard security procedure for online presences.
- IaaS:
- Standard security procedure as any on-premise infrastructures.
- Benefits from native administrative tools from the Cloud Provider.
20. Cloud provider: SaaS security
- SaaS:
- Web application security: OWASP’s Top 10
- Multi-tenancy: data isolation/leakage
- Data security: accessibility versus security trade-off
21. Cloud provider: PaaS security
- Similar security concerns as SaaS
- Complex security schemes due to potential third-party relationships.
- Development Lifecycle
- Users depend on PaaS providers to patch security issues of the individual tools.
22. Cloud provider: IaaS security
- Standard security measures.
- To Cloud Provider, cloud resources are on-premise.
- Concerns with virtual machines’ security
- Concerns with virtual networking security
Key Points
It depends!
There is never an easy answer to investment in infrastructure.