OpenMP: parallel regions and loop parallelism
Overview
Teaching: 0 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
Do we have to manually do everything?
Objectives
Know how to use parallel for pragma
Loop parallelism
- Very common type of parallelism in scientific code
- In previous trapezoid example, we calculate the division of iteration manually.
- An alternative is to use
parallel forpragma
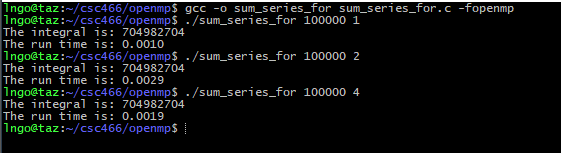
Hands-on 1: Sum series implementation
- In the EXPLORER window, right-click on
csc466/openmpand selectNew File.- Type
sum_series_for.cas the file name and hits Enter.- Enter the following source code in the editor windows:
- Save the file when you are done:
Ctrl-Sfor Windows/LinuxCommand-Sfor Macs- Memorize your key-combos!.
#include <omp.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { int N = atoi(argv[1]); int nthreads = atoi(argv[2]); int partial_sum[nthreads]; clock_t start, end; omp_set_num_threads(nthreads); start = clock(); #pragma omp parallel { int tid = omp_get_thread_num(); partial_sum[tid] = 0; #pragma omp for for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { partial_sum[tid] += i; } } end = clock(); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { sum += partial_sum[i]; } printf("The integral is: %d\n", sum); printf("The run time is: %.4f\n", ((double) (end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC); return 0; }
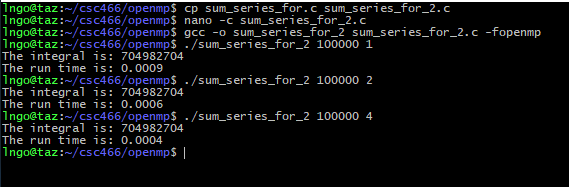
Hands-on 2: Improving sum series implementation
- In the EXPLORER window, right-click on
csc466/openmpand selectNew File.- Type
sum_series_for_2.cas the file name and hits Enter.- Enter the following source code in the editor windows:
- Save the file when you are done:
Ctrl-Sfor Windows/LinuxCommand-Sfor Macs- Memorize your key-combos!.
#include <omp.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { int N = atoi(argv[1]); int nthreads = atoi(argv[2]); int partial_sum[nthreads]; clock_t start, end; omp_set_num_threads(nthreads); start = clock(); #pragma omp parallel { int tid = omp_get_thread_num(); partial_sum[tid] = 0; int psum = 0; #pragma omp for for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { psum += i; } partial_sum[tid] = psum; } end = clock(); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { sum += partial_sum[i]; } printf("The integral is: %d\n", sum); printf("The run time is: %.4f\n", ((double) (end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC); return 0; }
Key Points
Parallel for allows simplification of code